1 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
Chih-Hao Chang
University of Texas at Austin
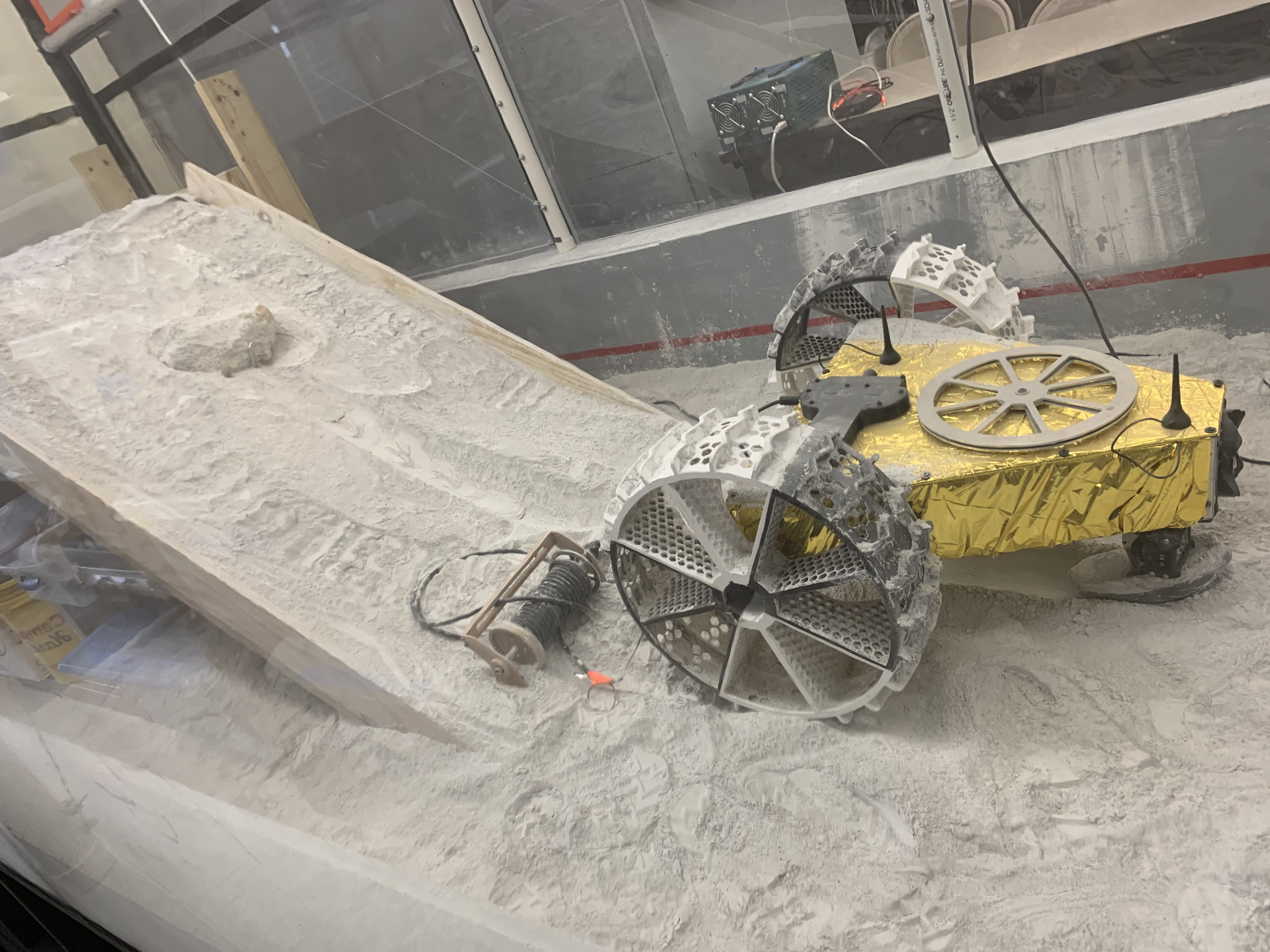
Establishing a permanent base on the moon is a critical step in the exploration of deep space. One significant challenge observed during the Apollo missions was the adhesion of lunar dust, which can build up on vehicle, equipment, and space suit. Highly fine and abrasive, the dust particles can have adverse mechanical, electrical, and health effects. The proposed research aims to develop a new class of hierarchical, heterogenous nanostructured coating that can passively mitigate adhesion of lunar particles. Using scalable nanolithography and surface modification processes, the geometry and material composition of the nanostructured surface will be precisely engineered to mitigate dust adhesion. This goal will be accomplished by: (1) construct multi-physical models to predict the contributions of various particle adhesion mechanisms, (2) develop scalable nanofabrication processes to enable precise control of hierarchical structures, and (3) develop nanoscale single-probe characterization protocols to characterize adhesion forces in relevant space environments. The proposed approach is compatible with roll-to-roll processing and the dust-mitigation coating can be transfer printed on arbitrary metal, ceramic, and polymer surfaces such as space suits, windows, mechanical machinery, solar panels, and sensor systems that are vital for long-term space exploration.